Omega 3, 6, and 9 – these are the most common terms every nutritionist and doctor talk about.
But did you know these fatty acids can also provide great benefits for healthy hair growth?
In this “Fatty Acids for Healthy Hair” series, you will learn everything you need to know about fatty acids in relation to hair. We will also cover some of the other fatty acids in more depth in separate articles.
Overall picture
First, let’s start with an overall picture:
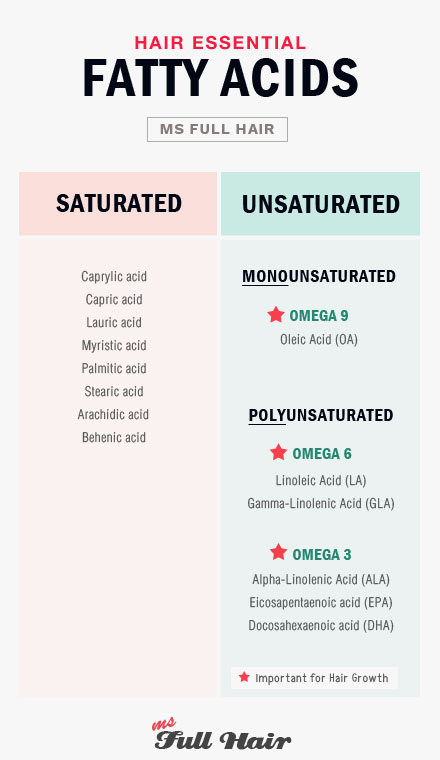
What is fat?
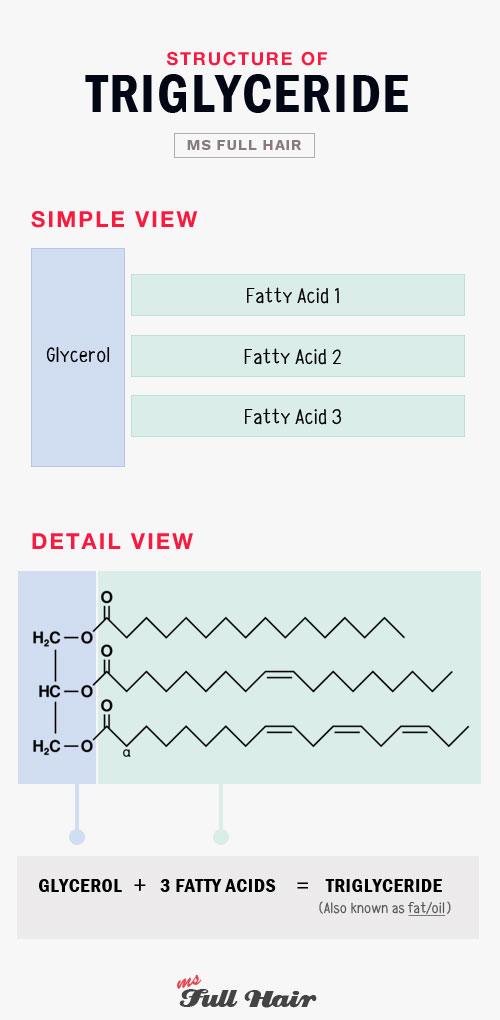
Fat is a naturally occurring molecule.
The scientific name of fat (or oil) is triglyceride. It has a glycerol base structure with 3 fatty acids attached like below:
What’s the difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Fat can be either saturated or unsaturated.
What differentiates these two is based on the bond structure.
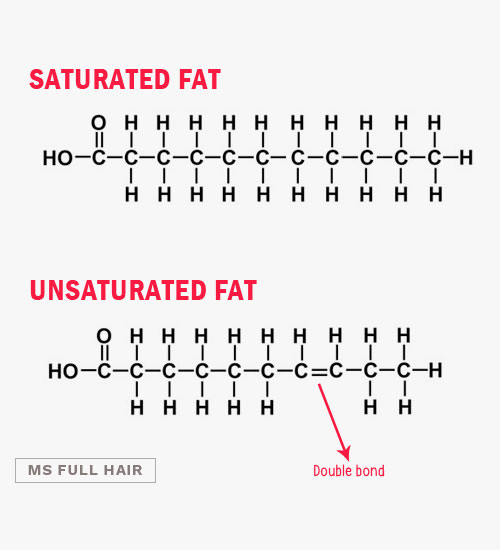
Saturated fat is made up of a carbon chain with single bonds, meaning each carbon (C) is saturated with hydrogen (H) atoms.
Its closely stacked structure makes saturated fat solid at room temperature and has a high smoking point (the most commonly understood example is fatty beef or pork).
Unsaturated fat contains a double bond carbon in the structure.
This means that not every carbon (C) is attached to hydrogen (H), resulting in fewer hydrogens. This makes the structure more curly and less packed, which is why unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature.
If there is one double bond in a fatty acid, it’s called monounsaturated.
If there is more than one double bond, it’s called polyunsaturated. An example of oil high in polyunsaturated fat include sunflower seed oil.
Carrier oils: Many carrier oils used for both hair and skin care contain a combination of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (also known as oleic acid and linolenic acid).
NOTE: The key difference between these saturated and unsaturated fats is the solidity at room temperature and the smoking point
- Saturated fats: Solid at room temperature, higher smoking point
- Unsaturated fats: Liquid at room temperature, lower smoking point
Are essential fatty acids saturated or unsaturated?
All essential fatty acids which include omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids are unsaturated.
Here are some of the examples:
- Carrier oils high in monounsaturated fats: Olive oil and sweet almond oil
- Carrier oils high in polyunsaturated fat: Evening primrose oil and grapeseed oil
Omega 3 fatty acids
Omega 3 is a polyunsaturated fatty acid that has the first double bond at the 3rd carbon location starting from the tail (omega) of the chemical chain (that’s why it’s called omega 3).
Omega 3 is an essential fatty acid because our body can’t make it on its own, thus we need to ingest it or use it as a topical application.
The most popular types of omega 3 fatty acids include:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): mainly from vegetables, plants, and nut-based oils (flaxseed oil, pumpkin seed oil, canola oil, etc)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): abundant in fish oils
- Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA): abundant in fish oils and alga
Omega 3 benefits for hair growth
Omega 3 fatty acids plays an important role in providing essential vitamins and minerals to hair follicles by keeping the liver healthy. Our blood goes through the liver which cleanses toxins and unwanted substances. Some of the blood then flows through and feed hair follicles, which is how follicles are able to grow.
Omega 3 fatty acids are also anti-inflammatory. They inhibit certain molecular production that can cause inflammatory reactions in our body. This property then helps prevent some of the most common scalp conditions such as flaky residue, dandruff, red and itchy scalp, all of which are due to scalp inflammation.
How much omega 3 per day is good for hair growth?
There is no official daily recommended amount of omega 3, but a study that involved 120 participants suffering female pattern hair loss showed great hair growth results after taking 460 mg of fish oil along with 460 mg of black currant oil (another great source rich in omega 3 and 6).
You can read more about it here and also see omega 3 hair growth before and after photos.
Takeaway
For stimulating hair growth, get omega 3 from dietary supplements
Omega 6 fatty acids
Omega 6 is a polyunsaturated fatty acid with the first double bond located at the 6th carbon atom in the chemical chain.
Similar to omega 3, omega 6 can only be obtained through foods or topical use since our body can’t produce it on our own. It’s also regarded as an essential fatty acid.
Two of the most popular omega 6 fatty acids for hair include:
- Linoleic acid (LA): Linoleic acid is THE molecule for acne-prone skin and inflamed and oily scalp. LA is found in many vegetable oils. Carrier oils high in linoleic acid include grapeseed oil and safflower oil
- Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA): Our body naturally converts linoleic acid into gamma-linoenic acid. Or you can also get GLA from dietary consumption such as evening primrose oil, black currant seed oil, and borage oil
Omega 6 benefits for hair growth
Gamma-linolenic acid and linoleic acid (omega 6 fatty acids) can prevent androgenic alopecia by down-regulating 5a reductase – the main cause of hair loss. When the 5a reductase enzyme is blocked, DHT hormones in the scalp also decrease, thus it prevents thinning hair and promotes hair growth.
A study also notes that alpha-linolenic acid (omega 3 fatty acids) helps with this inhibition. It’s a good idea to have both omega 6 and omega 3 for stimulating hair growth.
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) also has an anti-inflammatory property.
Evening primrose oil is high in GLA and also helps with thyroid hormone balance. So if you are experiencing hair thinning due to thyroid disease, evening primrose oil can help alleviate excessive fall out and put your hair back to normal healthy growth.
You’ll also want to consider black currant oil, which are high in both GLA of omega 6 (15-20%) and omega 3 (12-14%).
Takeaway
- For topical use, use carrier oils high in linoleic acid for hair growth and relieving scalp inflammation such as grapeseed oil
- For dietary use, take supplements high in GLA. The best source is evening primrose oil or black currant oil for stopping hair loss
Omega 9 fatty acids
Omega 9 is a monosaturated fatty acid with one double-bound located at the 9th carbon atom. Omega 9 is not an “essential” fatty acid, meaning our body produces it (in addition to consuming it from foods).
- Oleic acid is one of the most popular omega 9 fatty acids found in vegetable and nut oils including olive oil and macadamia oil.
Omega 9 benefits for hair growth
Oleic acid and linolenic acid are two important ingredients when it comes to skin and hair care.
Oleic acid (omega 9 fatty acid) is found in many vegetable oils and is often referred as “a skin penetration enhancer”. Studies show that oils high in oleic acid permeates into the skin and has deep hydrating properties by adding a moisturizing layer to minimize water loss.
This explains why there are so many cosmetic and hair care products that contain oleic acid as one of their main ingredients for deep nourishing and hydrating effects.
Takeaway
For topical use, use carrer oils high in oleic acid (omega 9 fatty acid) for nourishing and moisturizing properties such as olive oil. This works well if you have frizzy, brittle, and damaged hair.
Final takeaway
Each of omega 3, 6, and 9 have their own or combined beneficial properties for promoting hair growth.
When it comes to these fatty acids, one is not better than any other. Each fatty acid provides unique properties essential for healthy hair growth. Take them as supplements or use with a carrier oil.
Here is the final takeaway from the article:
2 Fatty acids important for dietary consumption for healthy hair growth
– Omega 3 fatty acid with high content of DHA/EPA such as this fish oil
– Omega 6 gamma linolenic acid such as evening primrose oil (this oil is also good for thyroid hormone balance)
2 Fatty acids important for topical application for encouraging hair growth
Omega 6 linoleic acid for inflamed (dandruff, itchiness, and redness) and oily scalp: It has a lighter texture and balances the high content of oleic acid existing on the skin/scalp.
Our recommendations of carrier oil high in linoleic acid is safflower oil, grape oil and evening primrose oil (yes – you can use evening primrose oil for topical application as well)
Omega 9 oleic acid for nourishing damaged and brittle hair strands: It has a velvety and richer consistency, perfect for deep moisturization of hair.
Good carrier oils high in oleic acid for hair growth are olive oil, sweet almond oil, and emu oil.